04. 前向传播
前向传播
MiniFlow 具有以下两个方法,可以帮助你定义和通过图表传播值:topological_sort() 和 forward_pass()。
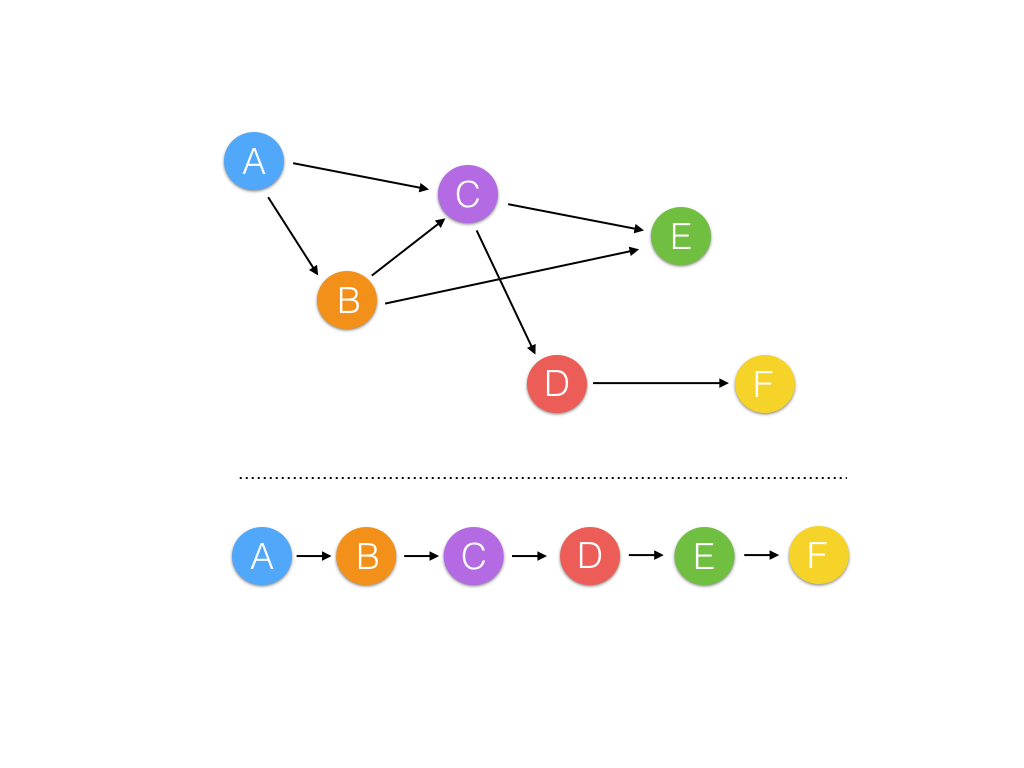
An example of topological sorting
为了定义你的网络,你需要定义节点的操作顺序。因为某些节点的输入取决于其他节点的输出,你需要按以下方式扁平化图表:在进行计算之前,每个节点的输入依赖项都已解决,这种技巧叫做拓扑排序。
topological_sort() 函数使用 Kahn 算法进行拓扑排序。该方法的细节方面并不重要,结果很重要;topological_sort() 返回一个排好序的节点列表,所有计算都可以按序进行。topological_sort() 传入 feed_dict,我们按此方法为 Input 节点设置初始值。feed_dict 由 Python 字典数据结构表示。以下是示例使用情况:
# Define 2 `Input` nodes.
x, y = Input(), Input()
# Define an `Add` node, the two above`Input` nodes being the input.
add = Add(x, y)
# The value of `x` and `y` will be set to 10 and 20 respectively.
feed_dict = {x: 10, y: 20}
# Sort the nodes with topological sort.
sorted_nodes = topological_sort(feed_dict=feed_dict)(你可以在下面的编程测验中找到 miniflow.py 中 topological_sort() 的源代码。)
你还可以使用方法 forward_pass(),该方法会实际地运行网络并输出一个值。
def forward_pass(output_node, sorted_nodes):
"""
Performs a forward pass through a list of sorted nodes.
Arguments:
`output_node`: The output node of the graph (no outgoing edges).
`sorted_nodes`: a topologically sorted list of nodes.
Returns the output node's value
"""
for n in sorted_nodes:
n.forward()
return output_node.value练习 1 - 向前传递值
请创建并运行此图表!
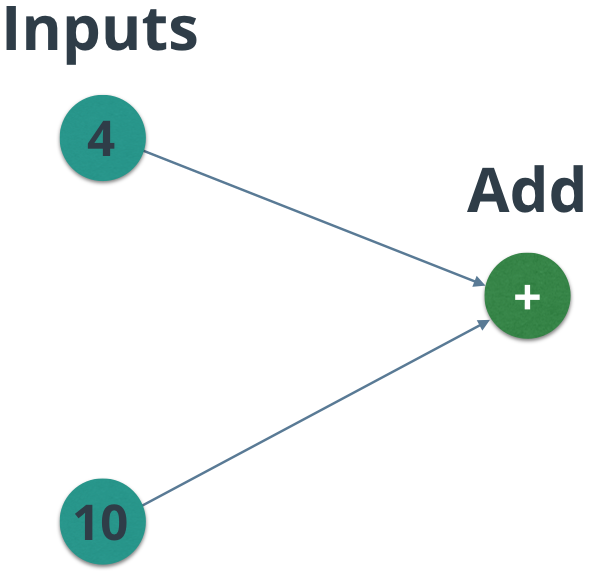
你将在此练习中运行的图表。但是节点值可能会改变!
设置
查看 nn.py 和 miniflow.py。
nn.py 中已经提供了神经网络架构。你需要完成 MiniFlow,使其能够运转。
对于此测验,请完成以下步骤:
- 打开下面的
nn.py。你不需要更改任何内容。我只是希望你能看下MiniFlow的工作方式。 - 打开
miniflow.py。完成Add类中forward的方法。要通过此测验,只需正确地实现forward。 - 通过点击“测试运行”测试你的网络。如果输出看起来正常,则点击“提交”。
(你将在下个页面看到解决方案)。
Start Quiz: